diabetic ketoacidosis workup|Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Cebu Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, . DFA Office of Consular Affairs
PH0 · Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state
PH1 · Diabetic ketoacidosis
PH2 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Evaluation and Treatment
PH3 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Practice Essentials, Background
PH4 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Workup
PH5 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
PH6 · DKA Recognition and ED Management
PH7 · Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Visit FAQs. Visit Online Services Fee Schedule. Visit Terms & Conditions. 1 While you can link your Hancock Whitney Bank debit and credit cards to any of these convenient payme11t options, we are not affiliated with nor do we endorse a specific wallet option. If you have any questions about a specific mobile wallet. please contact the payment .
diabetic ketoacidosis workup*******Diabetic ketoacidosis is typically characterized by hyperglycemia of over 250 mg/dL, a bicarbonate level of less than 18 mEq/L, and a of pH less than 7.30, with ketonemia and ketonuria.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of .diabetic ketoacidosis workup It is a life-threatening complication of diabetes and typically seen in patients with type-1 diabetes mellitus, though it may also occur .
Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, .Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is characterised by a biochemical triad of hyperglycaemia, ketonaemia, and acidaemia, with rapid symptom onset. Common symptoms and signs .Evidence. This topic is available for free. Treatment algorithm. Please note that formulations/routes and doses may differ between drug names and brands, drug . Insulin reverses diabetic ketoacidosis. In addition to fluids and electrolytes, insulin is given, usually through a vein. A return to regular insulin therapy may be . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS, also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state [HHNK]) are two of the . DKA management checklist. diagnostic evaluation ( more) Minimum evaluation for a patient with DKA: Electrolytes including Ca/Mg/Phos, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, EKG, . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS, also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state [HHNK]) are two of the . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and ketonuria.
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a complication of hyperglycemia associated with type 1 diabetes, characterized by. metabolic acidosis. gastrointestinal symptoms. altered mental status. serum ketones. Epidemiology. Demographics. often occur in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes. etiology. Insulin noncompliance. Update 2023: A prospective single center study including 177 adult patients with mild to moderate DKA found a significant reduction in median ED length of stay (-3.0, 95%CI -8.5 to -1.4) in patients who were . Workup Laboratory Studies. Plasma glucose. Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM) typically present with symptoms of uncontrolled hyperglycemia (eg, polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia). . Urine ketones are not reliable for diagnosing or monitoring diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), although they may be useful in screening to see whether .
Inadequate insulin in a child or adolescent with known diabetes (eg missed insulin doses, insulin pump failure). First presentation of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Illness. Assessment. History and examination are directed towards potential precipitants, assessment of severity, and detecting complications of DKA. Assessment of Dehydration Causes of ketoacidosis include starvation ketoacidosis, alcoholic ketoacidosis, and diabetic ketoacidosis. Clinical history is paramount in sorting these out. In patients with diabetes and alcoholism, it may be nearly impossible to sort out diabetic ketoacidosis versus alcoholic ketoacidosis (in this situation, the safest approach is . A diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis requires the patient's plasma glucose concentration to be above 250 mg per dL (although it usually is much higher), the pH level to be less than 7.30, and the .
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a medical emergency that occurs when there is not enough insulin in the body to control blood sugar (glucose) levels or the body cannot use the insulin effectively. Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose properly, so blood glucose levels get very high, and the body creates ketone bodies from fat as emergency .
Diabetic ketoacidosis, together with the major complication of cerebral edema, is the most important cause of mortality and severe morbidity in pediatric cases of diabetes, particularly at the time of first diagnosis. . Workup Approach Considerations. The following lab studies are indicated in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: Blood .Hypokalemia develops in in up to 80% of Diabetic Ketoacidosis cases with management; Low Serum Potassium on presentation suggests severe Hypokalemia. Must be corrected before Insulin initiation; Serum Chloride depressed (Hypochloremia) Serum Bicarbonate depressed (<15 to 18 mEq/L) Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS, also known as hyperosmotic hyperglycemic nonketotic state [HHNK]) are two of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. They are part of the spectrum of hyperglycemia, and each represents an extreme in the spectrum. In addition, ketoacidosis with mild .Frequency of signs and symptoms among 37 pediatric patients with diabetic ketoacidosis in Nigeria. May be the initial presenting of an unrecognized Type-1 diabetes mellitus patient; Signs/symptoms may include: . Consider infectious workup to identify trigger; Diagnosis. Hyperglycemia (>200) Acidosis. pH <=7.30 or bicarb <=15 +ketonemia (>1:2 .DKA that isn’t treated right away can cause a diabetic coma. The high acid in the blood causes the body not to work well, and can lead to a person becoming unconscious. When a child comes to the hospital with symptoms of DKA, the health care team will do blood tests and urine tests to know for . Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs when insufficient insulin results in blood sugar levels becoming too high. Without sufficient insulin, the body is unable to use blood sugar for energy. Instead, it . Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute, major, life-threatening complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and ketonuria.It occurs when absolute or relative insulin deficiency inhibits the ability of glucose to enter cells for utilization as metabolic fuel, the result being that the liver rapidly breaks down .Diabetic ketoacidosis, together with the major complication of cerebral edema, is the most important cause of mortality and severe morbidity in pediatric cases of diabetes, particularly at the time of first diagnosis. (See Pathophysiology and Prognosis.Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life threatening medical emergency. It is characterised by hyperglycaemia, dehydration, metabolic acidosis and ketonuria. The criteria for the diagnosis of DKA includes a blood sugar >14.0 mmol/l, presence of urinary or plasma ketones, a pH< 7.3 and a serum bicarbonate of less than 18 mmol/l. The main .
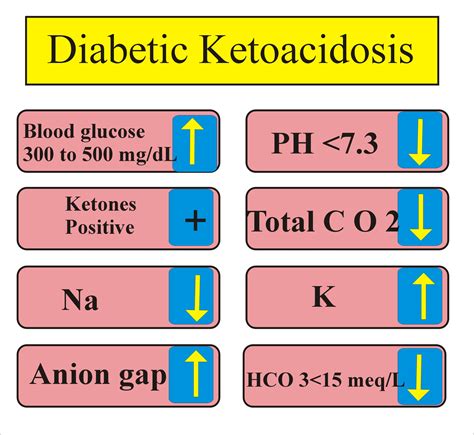
4.1 Workup; 4.2 Diagnosis; 5 Management; 6 Disposition; 7 See Also; 8 External Links; 9 References; Background Clinical Features Differential Diagnosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis; Alcoholic ketoacidosis; Starvation ketoacidosis; Evaluation Workup Diagnosis Management Disposition See Also

The influence of ketoacids on plasma creatinine assays in diabetic ketoacidosis. J Intern Med. 2000 Dec;248(6):511-7. https: . If indicated clinically, further sepsis workup should be performed. Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes .
Our high definition head scans are captured using the latest in photogrammetry technology with a dedicated 120 camera rig. Each scan goes through a rigorous cleaning, retopologizing and detailing process to ensure the highest level of .
diabetic ketoacidosis workup|Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis